학습목표 : 함수적 인터페이스를 이해하고 사용할 수 있다.
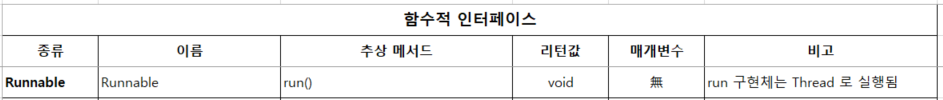
1. Runnable - run() 함수를 보유하며 리턴값과 매개변수가 없음.
The Runnable interface should be implemented by any class whose instances are intended to be executed by a thread. The class must define a method of no arguments called run.
package team.study._lamda.standardapi;
public class RunnableExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable ra = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
};
ra.run();
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
/* lamda expression */
Runnable runnable = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.start();
}
}
2. 자바8 함수적 인터페이스(Functional Interface)
java.util.function 표준 API 패키지로 제공.
이 패키지에서 제공하는 함수적 인터페이스의 목적은 메소드 또는 생성자의 매개 타입으로 사용되어
람다식을 대입할 수 있도록 하기 위함.
java.util.function 패키지의 함수적 인터페이스는 크게
Consumer, Supplier, Function, Operator, Predicate로 구분
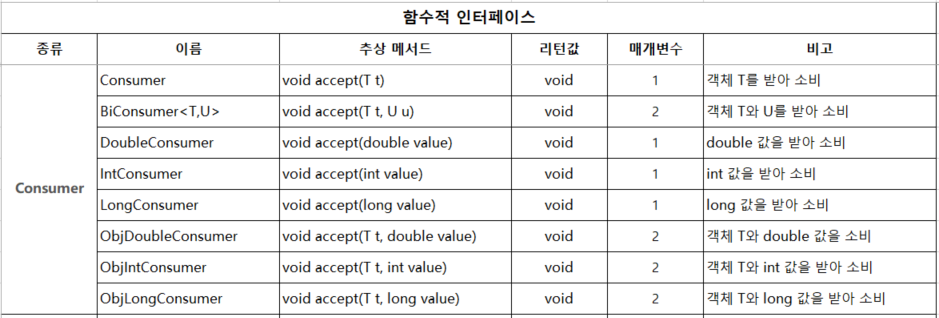
2.1 Consumer (소비자) - 리턴값 없음 void
package team.study._lamda.standardapi;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class ConsumerSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Consumer<String> consumer = (t) -> System.out.printf("Parameter is %s \n", t);
consumer.accept("Consumer");
BiConsumer<String, Integer> biConsumer = (t, u) -> {
String name=t;
int age = u;
System.out.printf("Name is %s . Age is %d", name, age);
};
biConsumer.accept("Hong", 20);
}
}
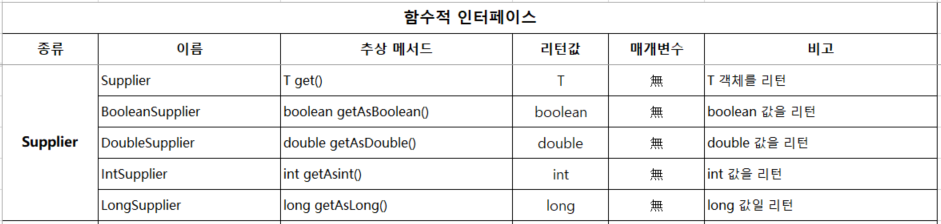
2.2 Supplier (공급자) - 리턴값 있음
package team.study._lamda.standardapi;
import java.util.function.IntSupplier;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class SupplierSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Supplier<String> supplier = () -> { return "Hello Supplier"; };
Supplier<String> supplier = () -> "Hello Supplier";
System.out.println(supplier.get());
IntSupplier intSupplier = () -> {
return 20;
};
System.out.println(intSupplier.getAsInt());
}
}
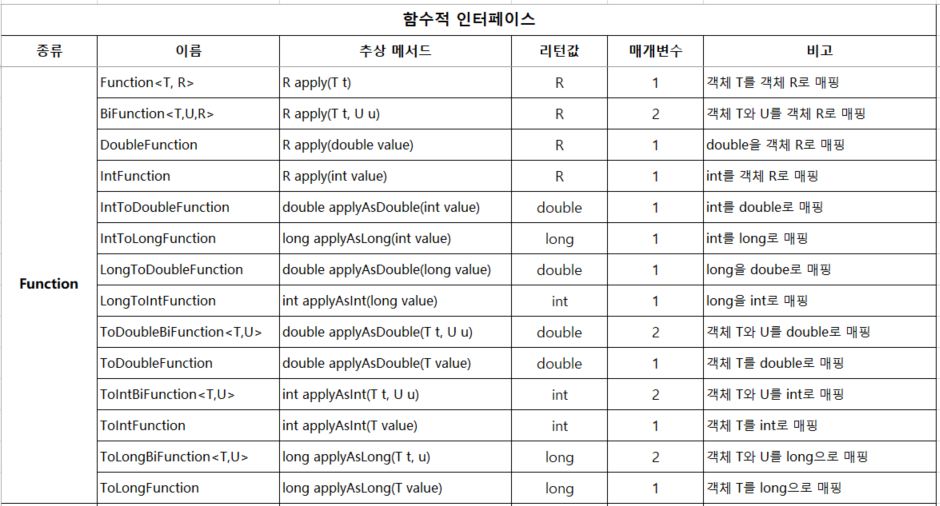
2.3 Function (함수) - 인자의 타입을 변형하여 새로운 타입으로 리턴, 형변환 전용 함수형 인터페이스
package team.study._lamda.standardapi;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class FunctionSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<String, String> ff = (t) -> t;
System.out.printf("Result1 is %s \n",ff.apply("HongGilDong"));
Function<Friend, String> f = (t) -> t.name;
Friend friend = new Friend();
System.out.printf("Result2 is %s \n",f.apply(friend));
Function<Friend, Integer> f2 = (t) -> t.age;
System.out.printf("Result3 is %s \n",f2.apply(new Friend()));
}
}
class Friend{
String name = "HongGilDong";
int age = 20;
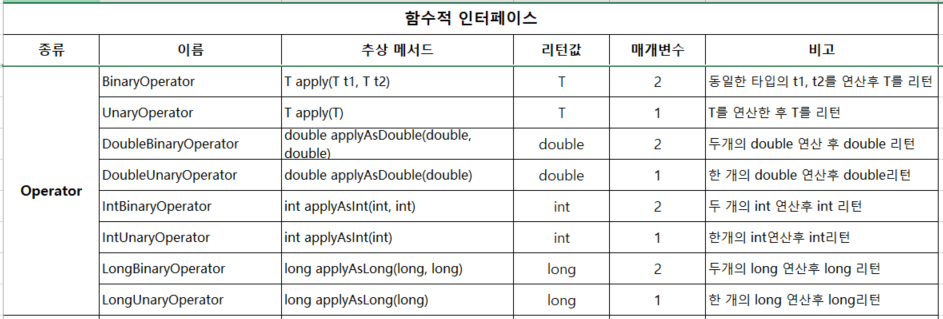
}2.4 Operator (조작/교환) -매개인자의 타입과 리턴값의 타입이 동일, Function과 동일한 형태의 applyXXX라는 메소드를 가지고 있다.
package team.study._lamda.standardapi;
import java.util.function.BinaryOperator;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
public class OperatorSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryOperator<Integer> b = (t1, t2) ->{
int sum = t1 + t2;
return sum;
};
System.out.println("Sum is "+b.apply(10, 20));
UnaryOperator<String> u = t -> t;
System.out.println(u.apply("Hello Unary"));
UnaryOperator<String> u2 = (t) -> {
Friend2 f = new Friend2();
return f.name;
};
System.out.println("Result is "+u2.apply("Hi"));
}
}
class Friend2{
String name = "HongGilDong";
int age = 20;
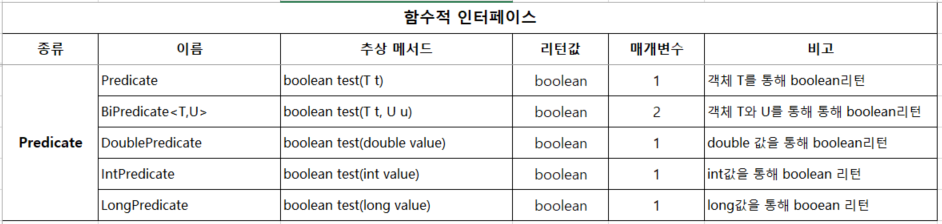
}2.5 Predicate - 매개 값을 이용하여 true , false 를 리턴한다.
package team.study._lamda.standardapi;
import java.util.function.BiPredicate;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredicateSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
/* 매개변수가 KIM 이면 true */
Predicate<String> p = t ->{
if(t.equals("KIM")){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
};
System.out.println("Result is "+p.test("KIM"));
/* 두 숫자가 1~9 일때 true */
BiPredicate<Integer, Integer> b = (t,u) ->{
if(t>0 && u<10) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
};
System.out.println("Result is "+b.test(5,19));
}
}
참고 블로그 - https://www.hanumoka.net/2018/11/24/java-20181124-java-lambda2/
java - 함수형 인터페이스 API(람다의 활용1)
들어가기자바의 람다는 자바언어에서 쉽고 간편하게 함수를 선언해서 사용하기위한 수단이다.하지만 자바는 객체 지향언어이고 기본적인 프로그래밍의 단위는 Class이다. 자바에서 구현하는 함
www.hanumoka.net
'Java > Lambda Expressions' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 예제로 배워보기 - 람다 & MethodReference(더블콜론) (1) (0) | 2021.07.18 |
|---|---|
| 예제로 배워보기 - 람다(1) (0) | 2021.07.17 |
| [Lamda Expression] Anonymous Classes -> Lamda Expression (0) | 2021.05.23 |
| [Anonymous Classes] 람다가 있기전 익명클래스가 있었다. (0) | 2021.05.23 |
| [Lambda Expressions] 소개 (0) | 2021.05.23 |